

Glucocorticoids are essential for some physiological actions of other hormones. 17-hydroxypregnenolone then moves into the endoplasmic reticulum and is converted into 17 hydroxyprogesterone. In the mitochondria, pregnenolone forms 17-hydroxypregnenolone by the enzyme 17 alpha-hydroxylase.
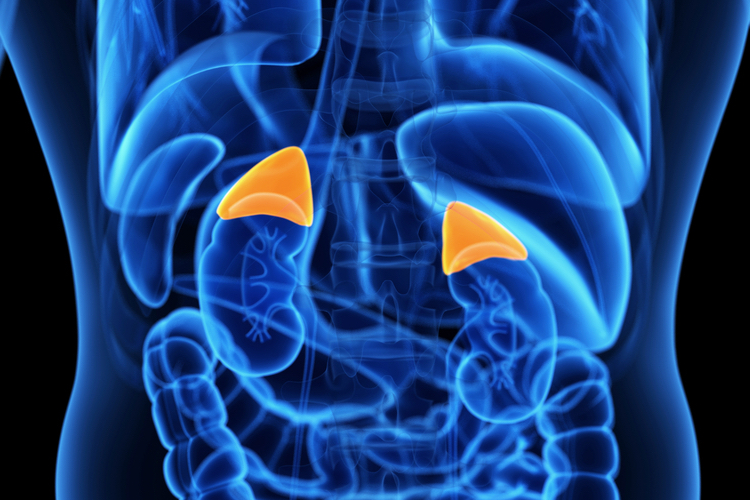
The main glucocorticoid formed are cortisol and corticosterone. Zona reticularis also contributes to this. These vessels originate from two lymphatic plexuses – one deep to the capsule, and the other in the medulla.The synthesis of glucocorticoids occurs mainly in the zona fasciculata of the adrenal cortex. Lymph drainage is to the lumbar lymph nodes by adrenal lymphatic vessels. Sympathetic innervation to the adrenal medulla is via myelinated pre-synaptic fibres, mainly from the T10 to L1 spinal cord segments. The adrenal glands are innervated by the coeliac plexus and greater splanchnic nerves. The right adrenal vein drains into the inferior vena cava, whereas the left adrenal vein drains into the left renal vein. Right and left adrenal veins drain the glands. Inferior adrenal artery – arises from the renal arteries.Middle adrenal artery – arises from the abdominal aorta.Superior adrenal artery – arises from the inferior phrenic artery.The adrenal glands have a rich blood supply via three main arteries: Chromaffin cells also secrete enkephalins which function in pain control. These hormones produce a ‘ flight-or-fight‘ response. It contains chromaffin cells, which secrete catecholamines (such as adrenaline) into the bloodstream in response to stress. The medulla lies in the centre of the gland, and is dark brown in colour. Fig 3 - Histological appearance of the cortex and medulla of the adrenal gland. Fig 2 - Posterior view of the abdomen, demonstrating the anatomical relations of the adrenal glands. It also secretes a small amount of corticosteroids. Zona reticularis – produces and secretes androgens such as dehydroepiandrosterone (DHES).It also secretes a small amount of androgens. Zona fasciculata – produces and secretes corticosteroids such as cortisol.Zona glomerulosa – produces and secretes mineralocorticoids such as aldosterone.Functionally, the cortex can be divided into three regions (superficial to deep): It secretes two cholesterol derived hormones – corticosteroids and androgens. The cortex and medulla synthesise different hormones. Medulla – derived from the ectodermal neural crest cells.Cortex – derived from the embryonic mesoderm.They are two separate endocrine glands, with different embryological origins: The outer cortex and inner medulla are the functional portions of the gland. The adrenal glands consist of an outer connective tissue capsule, a cortex and a medulla. Veins and lymphatics leave each gland via the hilum, but arteries and nerves enter the glands at numerous sites.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
